Digital Light Processing (DLP)
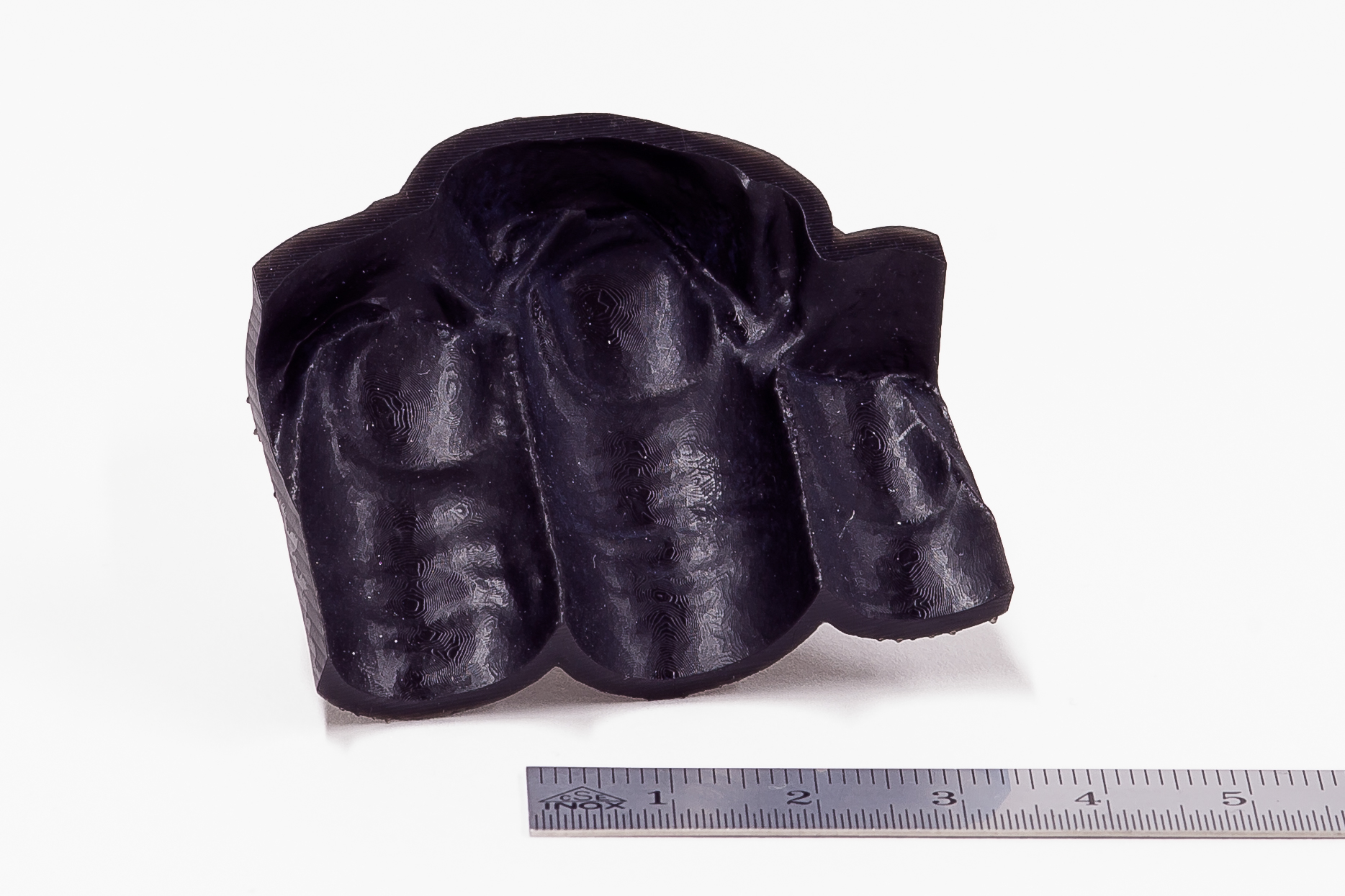
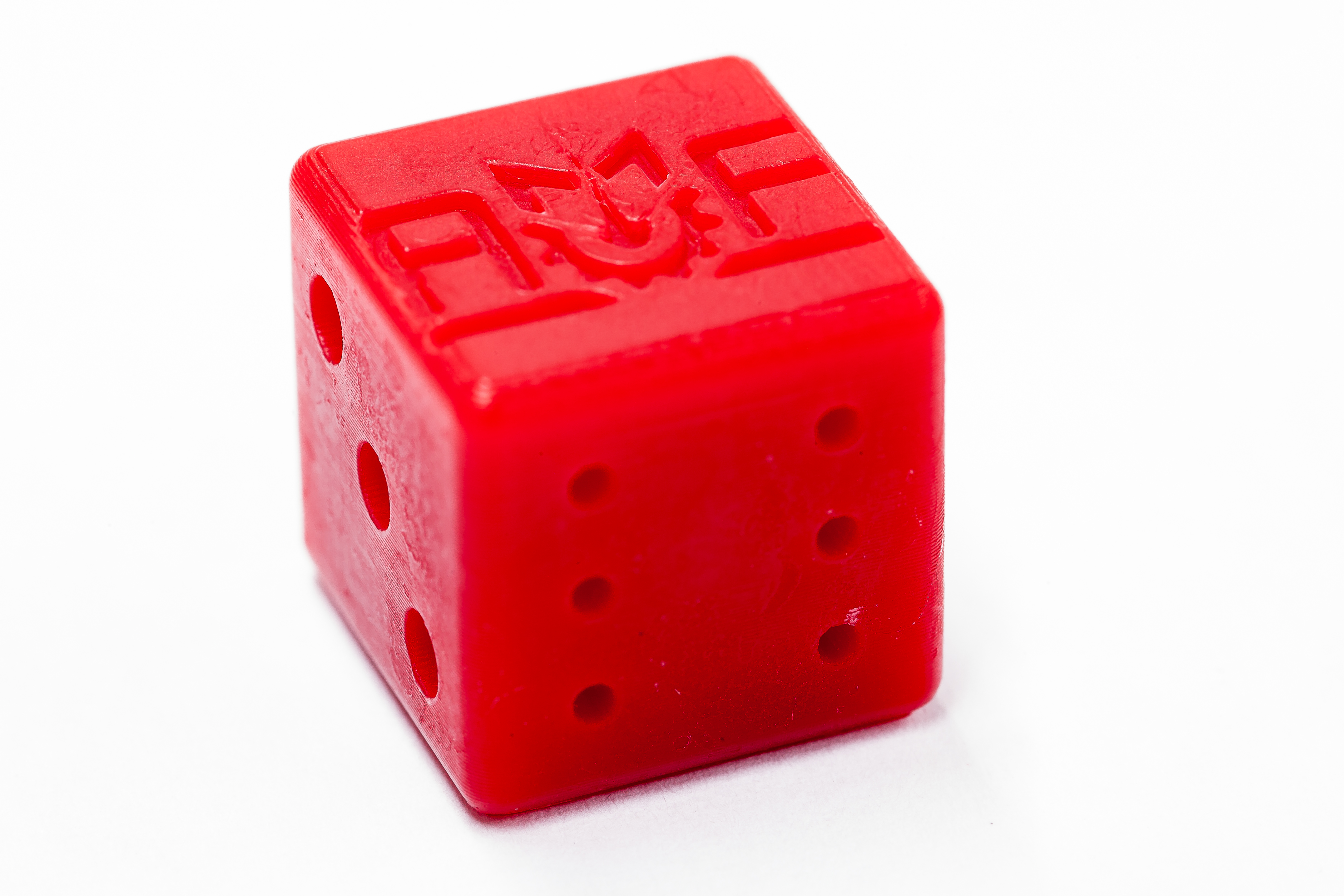
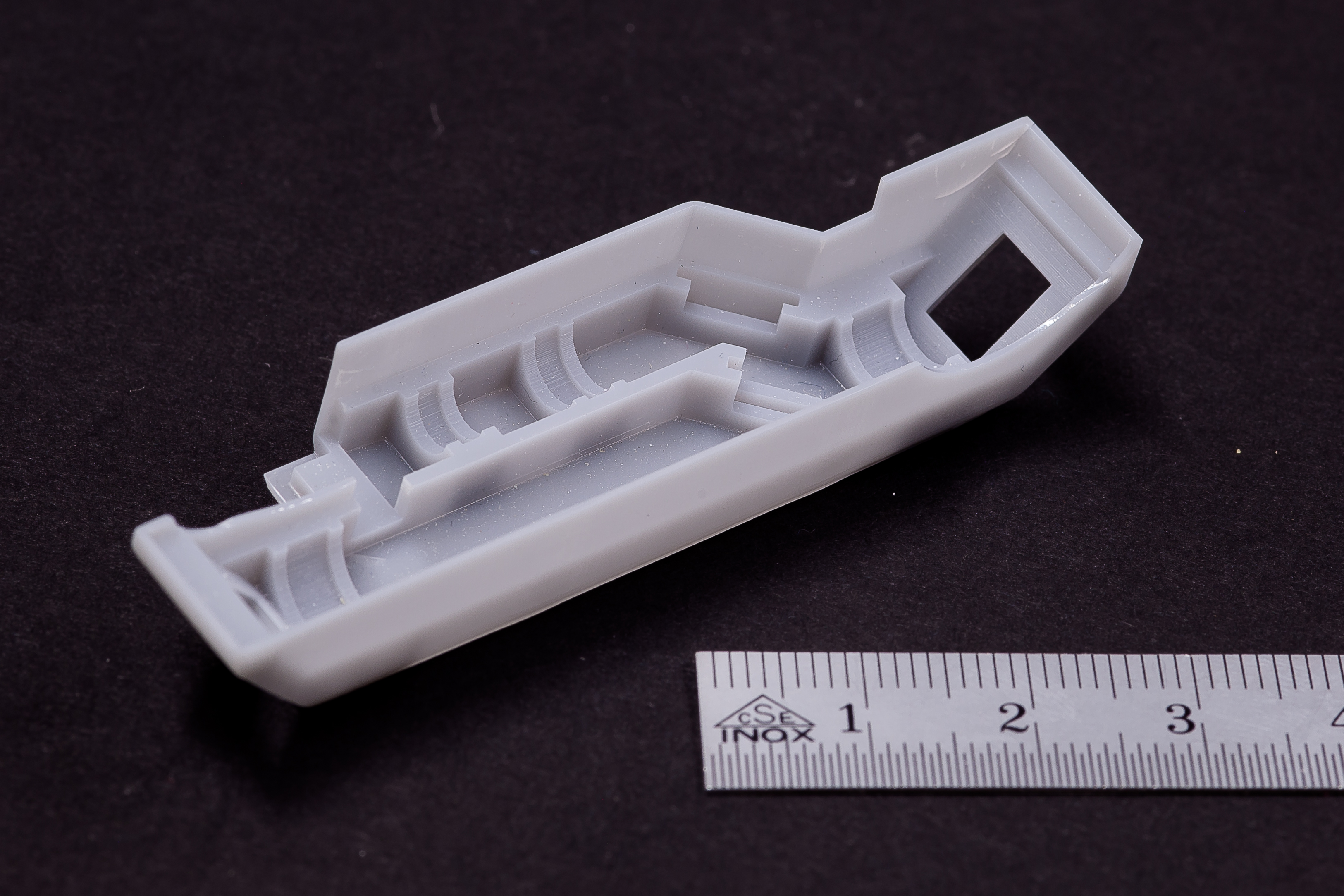
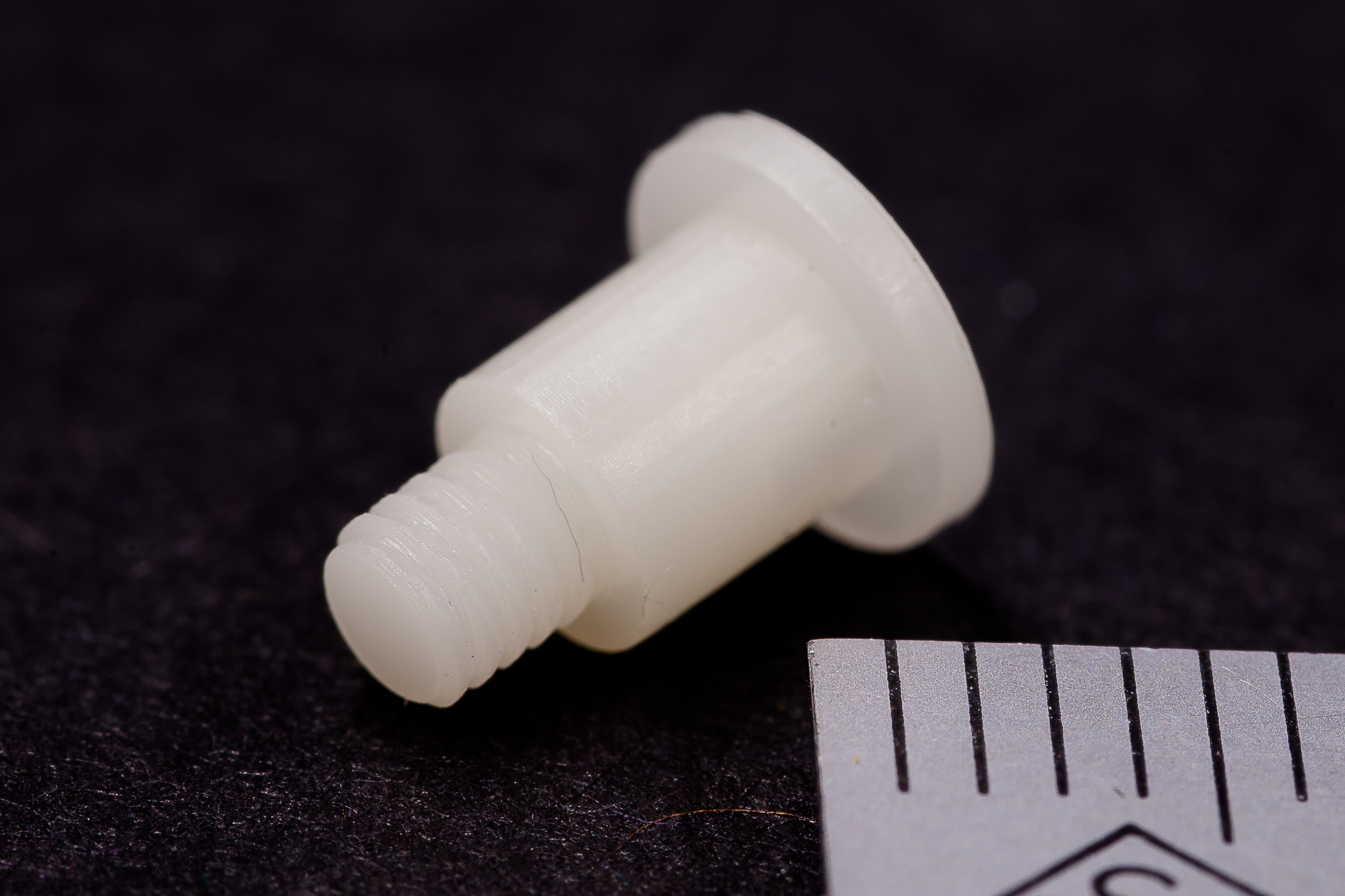
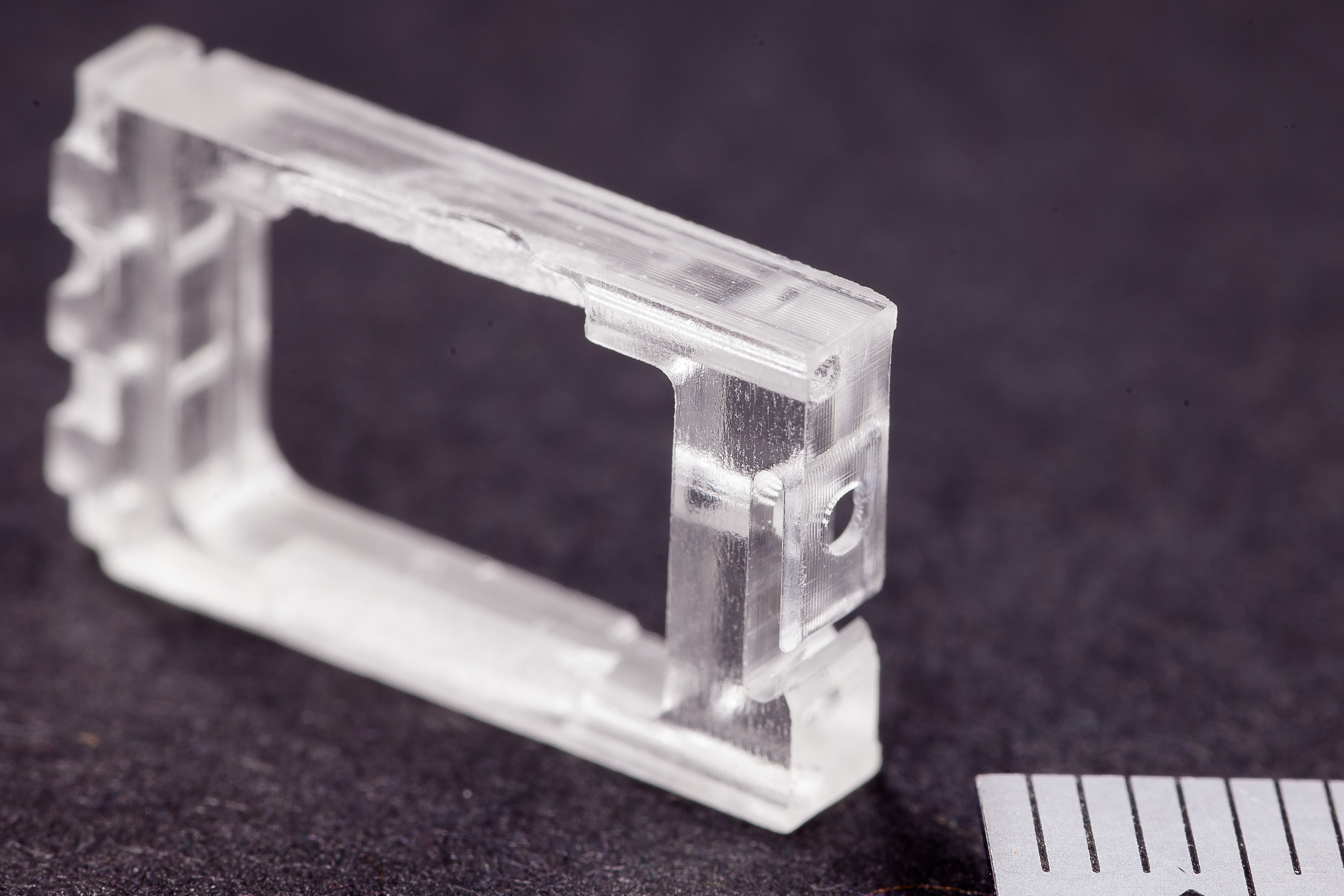
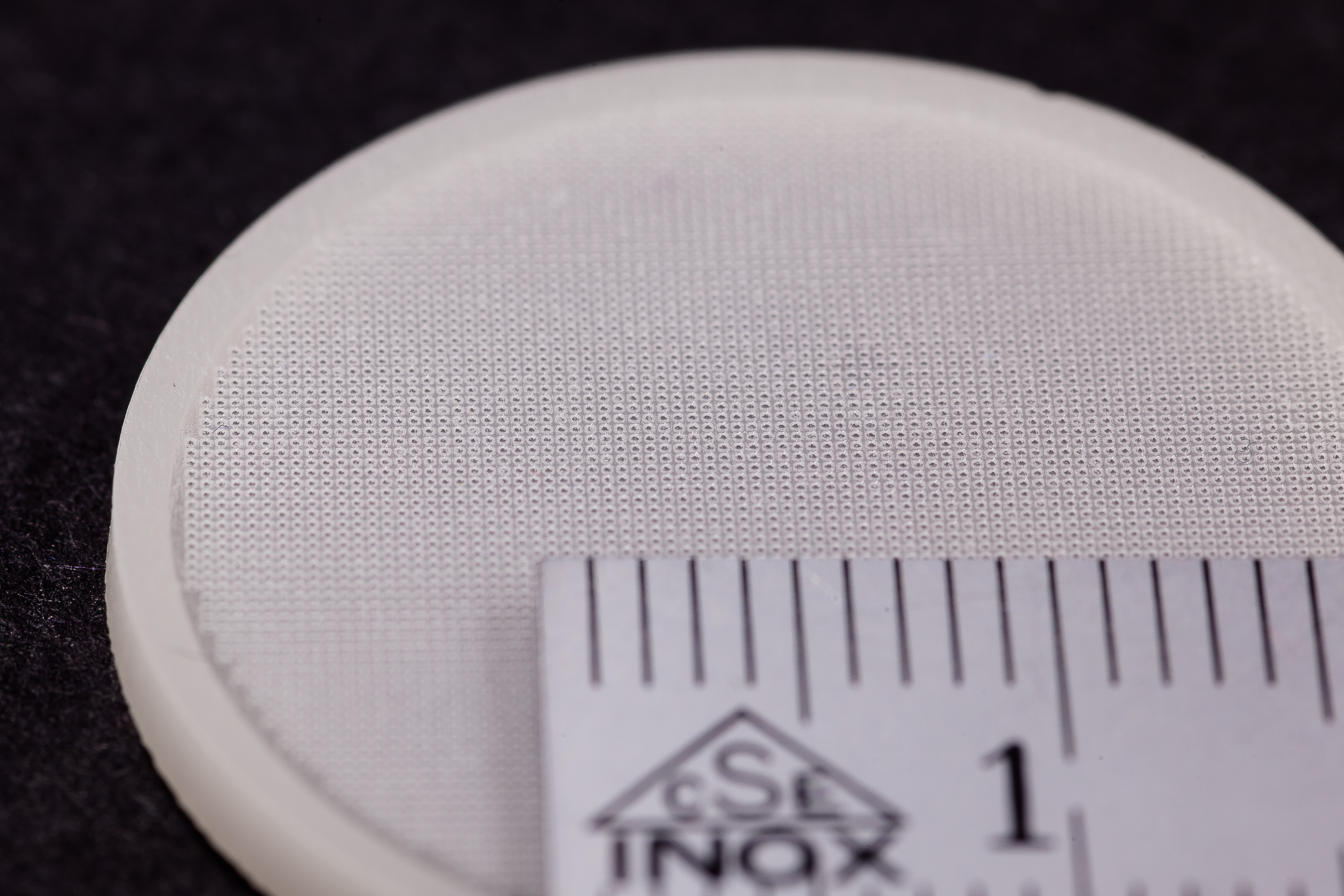
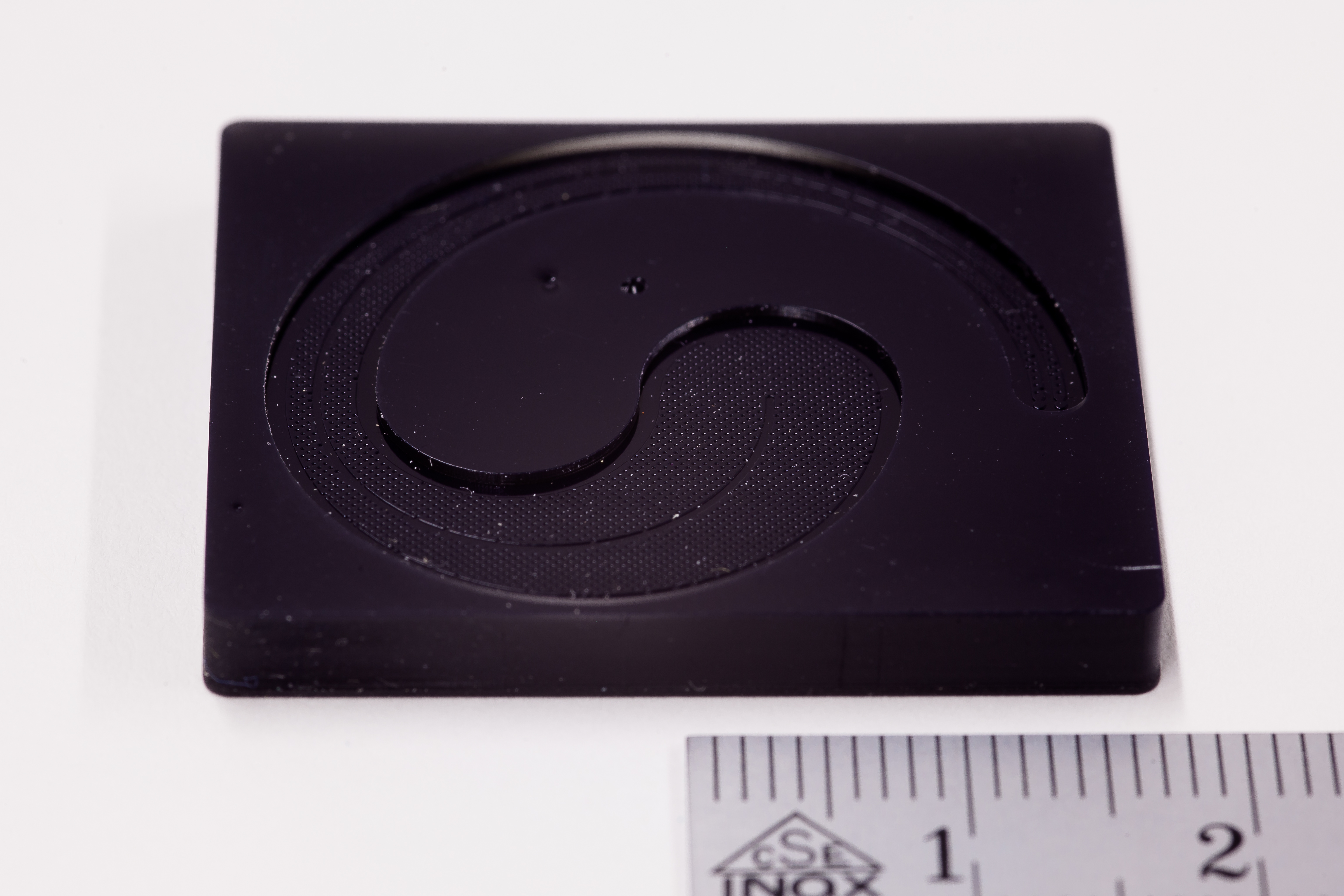
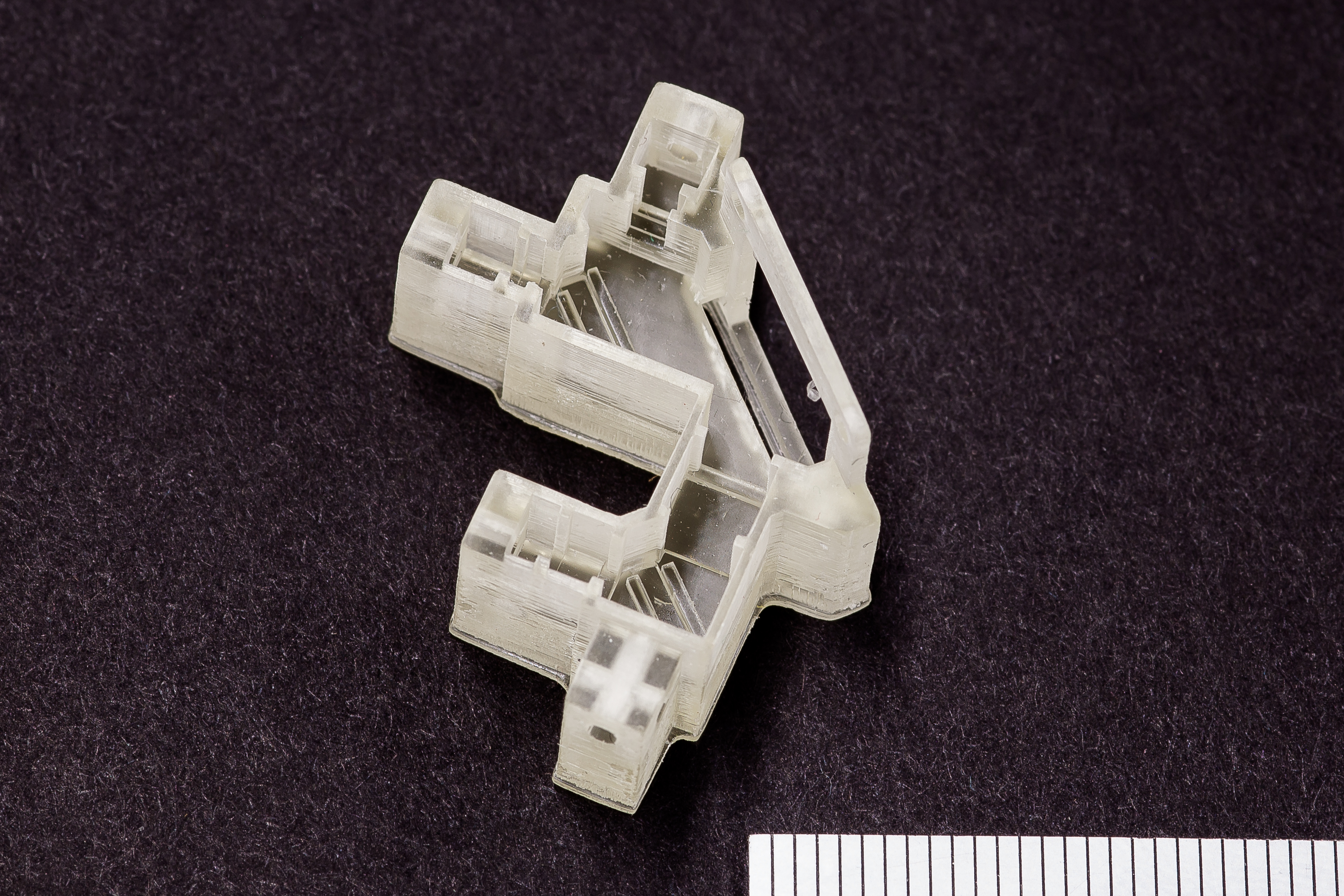
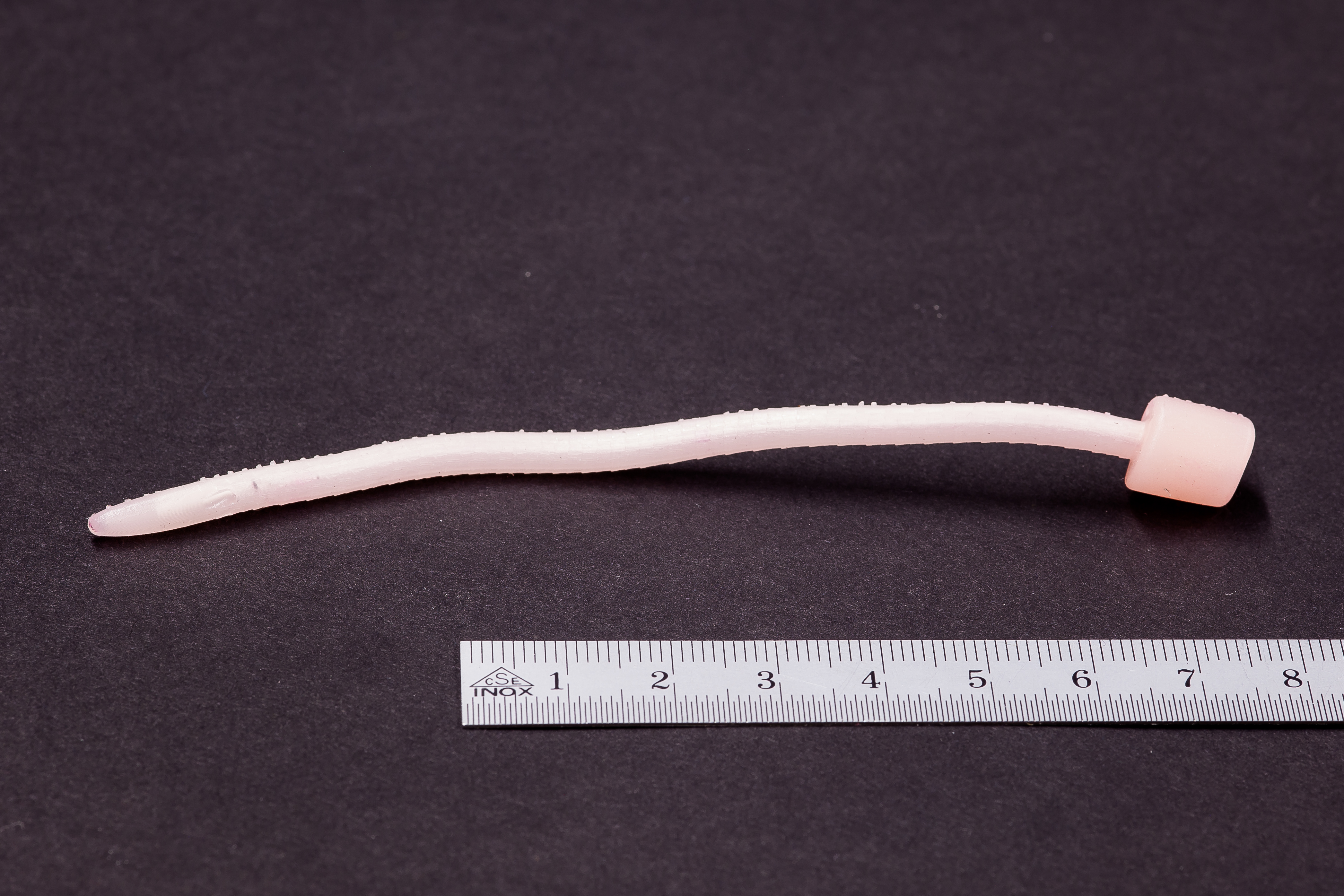
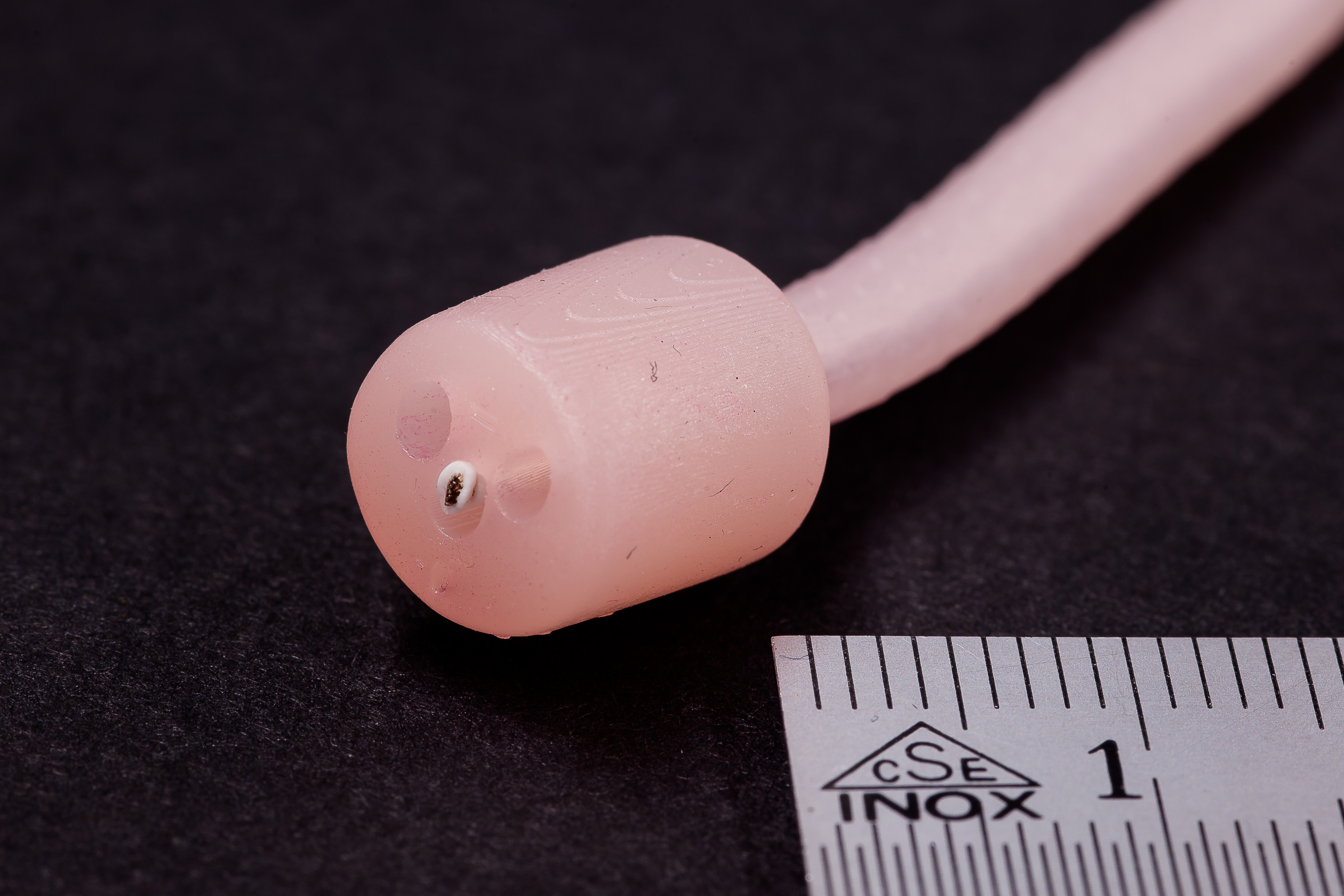
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is an AM technology that’s widely used within orthoplastic and dental manufacturing techniques because of the high accuracy and consistency it can achieve. DLP parts are created from a wide variety of photopolymers.
Functional Principle
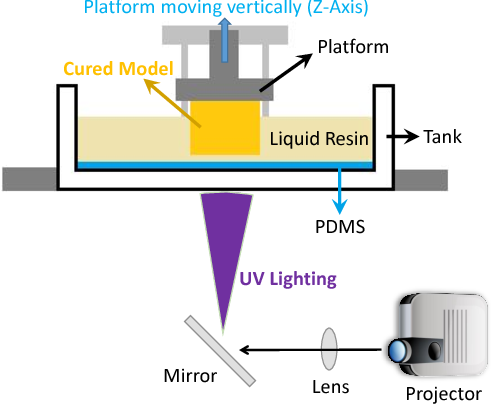
Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing process that focuses an ultraviolet (UV) light on a vat of plastic (photopolymer) resin. Through a process known as photo-polymerization, chains of molecules are linked together when exposed to the UV light, hardening them into solid resin layer by layer. The UV light continues this process through the entire vat of resin, using a DLP projector for curing and solidifying the resin to match the design of the CAD file. Structural supports are created during the pre-build setup process and manually removed after the print is completed. The parts are then washed in a solvent solution to remove uncured resin, and then receive a final post cure in a UV light oven.
Advantages / Disadvantages DLP
DLP offers higher resolution than many other additive manufacturing technologies, allowing customers to manufacture parts with fine details and surface finishes. The DLP technology is a highly-versatile platform for making custom parts in prototype and production settings, often acting as a stand-in for injection molded parts.
The high resolution and fast build speed is widely used in orthodontics and audiology. Medical device Class IIa materials are available and open up new possibilities for parts and tools in biology research.
Our open material system is also compatible with specialty resins, e.g., PEGDA hydrogels. The materials have often to be self developed and build parameters must be determined by tests. Many scientific puplications can therefor be found (search keywords: DLP 3D cell culture, DLP tissue engineering scaffolds etc.).
A disadvantage is however that the DLP technology works with photopolymers which are not stable over extended time and have not well defined mechanical properties. Medical grade materials and high performance resin formulations are expensive.
Ideal applications for DLP
- Small parts with smooth surfaces and fine details
- Prototypes for functional testing
- Exemplary for copying techniques such as injection molding and PDMS casting
- Low-volume production of complex small geometries
- Bioprinting with photocurable resin formulations (BYO material 385nm)